无限循环 ViewPager setCurrentItem 导致 ANR 分析
通过 adapter 的 getCount 返回一个足够大的数字,再初始化显示的item在中间位置,那么用户在左右滑动能够模拟出一个循环的显示界面。
2. 调用 setCurrentItem 卡顿 当我们设置的 getCount 是一个较小的数字时,调用该方法总能快速跳转到目标位置,但是 getCount 是一个大数,如 Integer.MAX_VALUE,那么在调用跳转时,很容易触发 anr。
2.1 源码分析 设置显示的item角标,最终调用 void setCurrentItemInternal(int item, boolean smoothScroll, boolean always, int velocity) 这个函数,看下这个方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 void setCurrentItemInternal(int item, boolean smoothScroll, boolean always, int velocity) { if (mAdapter == null || mAdapter.getCount() <= 0) { setScrollingCacheEnabled(false); return; } if (!always && mCurItem == item && mItems.size() != 0) { setScrollingCacheEnabled(false); return; } if (item < 0) { item = 0; } else if (item >= mAdapter.getCount()) { item = mAdapter.getCount() - 1; } final int pageLimit = mOffscreenPageLimit; //======================================================== //这个设置是最后铺满画面的判定,但如果是大数,这里就是一个隐藏的 ANR //======================================================== if (item > (mCurItem + pageLimit) || item < (mCurItem - pageLimit)) { // We are doing a jump by more than one page. To avoid // glitches, we want to keep all current pages in the view // until the scroll ends. for (int i = 0; i < mItems.size(); i++) { mItems.get(i).scrolling = true; } } final boolean dispatchSelected = mCurItem != item; if (mFirstLayout) { // We don't have any idea how big we are yet and shouldn't have any pages either. // Just set things up and let the pending layout handle things. mCurItem = item; if (dispatchSelected) { dispatchOnPageSelected(item); } requestLayout(); } else { //重要方法,添加移除item!ANR的分析重点 populate(item); //滑动到目标点 scrollToItem(item, smoothScroll, velocity, dispatchSelected); } }
上面可以看到,首先会先根据当前位置和目标位置距离判断是否需要滑动item,如果是滑动一页,不会触发设置scrolling,假如超过 pageLimit 泽一定会设置 scrolling = true。
第二个方法是 populate(item),用于移除看不见的item,添加新的item,下面部分代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 void populate(int newCurrentItem) { //...省略很多代码 // Fill 3x the available width or up to the number of offscreen // pages requested to either side, whichever is larger. // If we have no current item we have no work to do. if (curItem != null) { float extraWidthLeft = 0.f; int itemIndex = curIndex - 1; ItemInfo ii = itemIndex >= 0 ? mItems.get(itemIndex) : null; final int clientWidth = getClientWidth(); final float leftWidthNeeded = clientWidth <= 0 ? 0 : 2.f - curItem.widthFactor + (float) getPaddingLeft() / (float) clientWidth; //=========================== //curIndex 是 mItem 的最后一个item的位置,经过上面处理,已经在原来基础上增加了一个 //ii 是我们现在页面显示的item,这里处理当前页面之前的item是否需要销毁 //这里也很明显看出运算次数为 pos 次,当设置是一个大数是,2^32 ≈ 8^10 约等于 10^10 //那么这里将执行总数的一半次数,估计 10^9 次 //=========================== for (int pos = mCurItem - 1; pos >= 0; pos--) { if (extraWidthLeft >= leftWidthNeeded && pos < startPos) { //当 ii 为null时,能够跳出循环,ii的更新在下面的判断块中 if (ii == null) { break; } //只有条件成立才会更新ii,但上面说到,如果更新的位置在pageLimit之内, //scrolling 为false,超出则是true,超出的时候为了保证界面能完全填充 //也就是说无法跳出循环,所以在大数的时候,这里才是导致 ANR 的根本原因 if (pos == ii.position && !ii.scrolling) { mItems.remove(itemIndex); mAdapter.destroyItem(this, pos, ii.object); if (DEBUG) { Log.i(TAG, "populate() - destroyItem() with pos: " + pos + " view: " + ((View) ii.object)); } itemIndex--; curIndex--; ii = itemIndex >= 0 ? mItems.get(itemIndex) : null; } } else if (ii != null && pos == ii.position) { extraWidthLeft += ii.widthFactor; itemIndex--; ii = itemIndex >= 0 ? mItems.get(itemIndex) : null; } else { ii = addNewItem(pos, itemIndex + 1); extraWidthLeft += ii.widthFactor; curIndex++; ii = itemIndex >= 0 ? mItems.get(itemIndex) : null; } } float extraWidthRight = curItem.widthFactor; itemIndex = curIndex + 1; if (extraWidthRight < 2.f) { ii = itemIndex < mItems.size() ? mItems.get(itemIndex) : null; final float rightWidthNeeded = clientWidth <= 0 ? 0 : (float) getPaddingRight() / (float) clientWidth + 2.f; //这里同理,上面是判断设置的新页面在右边时,对当前页的左边进行处理 //下面代码是对当前页面右边的处理,一般执行次数为 pageLimit //如果新页面位置在当前页的右边,下面只会执行 pageLimit 次就跳出循环,因为pos+pageLimit 后的ii是null //同理,如果新页面在当前页的左边,上面也只会执行1次就跳出,因为 pos-pageLimit 的ii是null for (int pos = mCurItem + 1; pos < N; pos++) { if (extraWidthRight >= rightWidthNeeded && pos > endPos) { if (ii == null) { break; } if (pos == ii.position && !ii.scrolling) { mItems.remove(itemIndex); mAdapter.destroyItem(this, pos, ii.object); if (DEBUG) { Log.i(TAG, "populate() - destroyItem() with pos: " + pos + " view: " + ((View) ii.object)); } ii = itemIndex < mItems.size() ? mItems.get(itemIndex) : null; } } else if (ii != null && pos == ii.position) { extraWidthRight += ii.widthFactor; itemIndex++; ii = itemIndex < mItems.size() ? mItems.get(itemIndex) : null; } else { ii = addNewItem(pos, itemIndex); itemIndex++; extraWidthRight += ii.widthFactor; ii = itemIndex < mItems.size() ? mItems.get(itemIndex) : null; } } } calculatePageOffsets(curItem, curIndex, oldCurInfo); mAdapter.setPrimaryItem(this, mCurItem, curItem.object); } //...省略很多代码 }
上面注释说明非常清楚,通过对 pos 和scrolling 判断,来决定是否销毁当前页的前/后数据,这里程序只会循环 currentItem 次,原本我猜测即使空转,那应该也会很快处理完成,但在大数面前,任何的空转都应当理性对待。
假设 1w 次循环耗时为0.04ms,那么被放大10^5,也会达到4s,当设置为大数时,这个循环的时间不可忽视。
为了更加严谨,我在void populate(int newCurrentItem) 前后加入时间埋点,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @Aspect public class AspectVp { private long time = 0; @Before("call(void populate(..))") public void beforePopulate(JoinPoint joinPoint) { if (joinPoint.getArgs().length > 0) { Log.d("zhou", "AspectVp [before populate >> " + (time = System.currentTimeMillis())); } } @After("call(void populate(..))") public void afterPopulate(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { if (joinPoint.getArgs().length > 0) { long t = System.currentTimeMillis(); Log.i("zhou", "AspectVp [after populate >> " + t + " === spend = " + (t - time) + " ms"); } } }
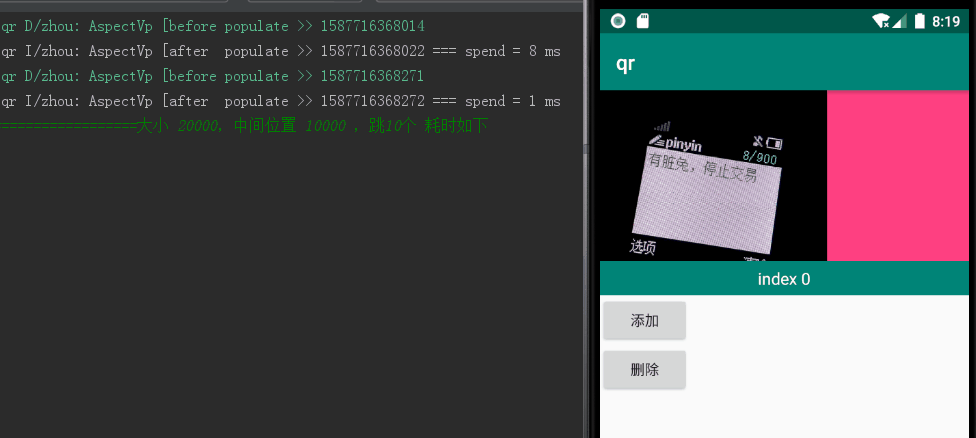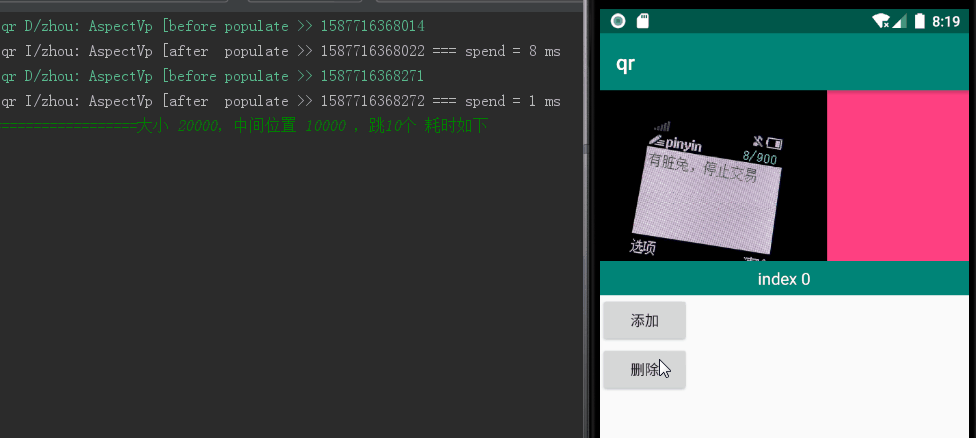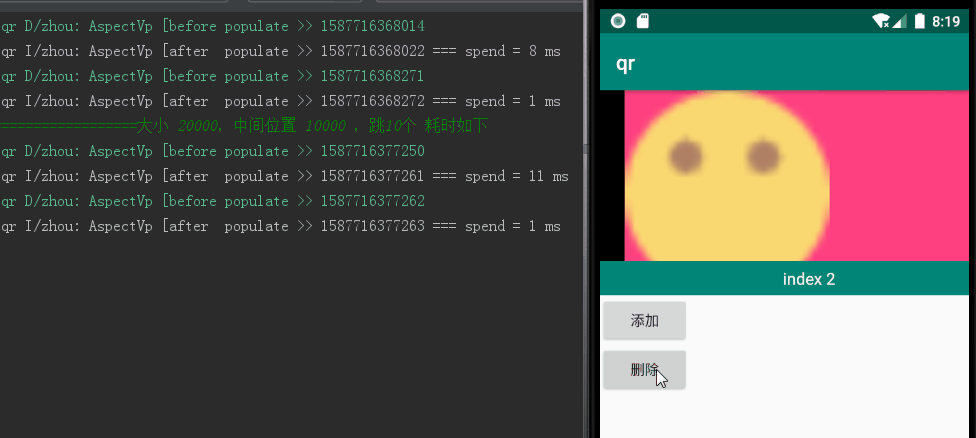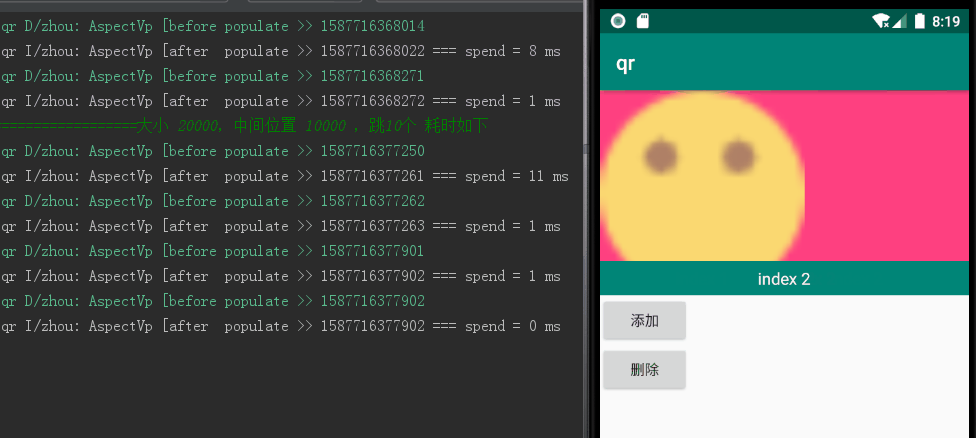
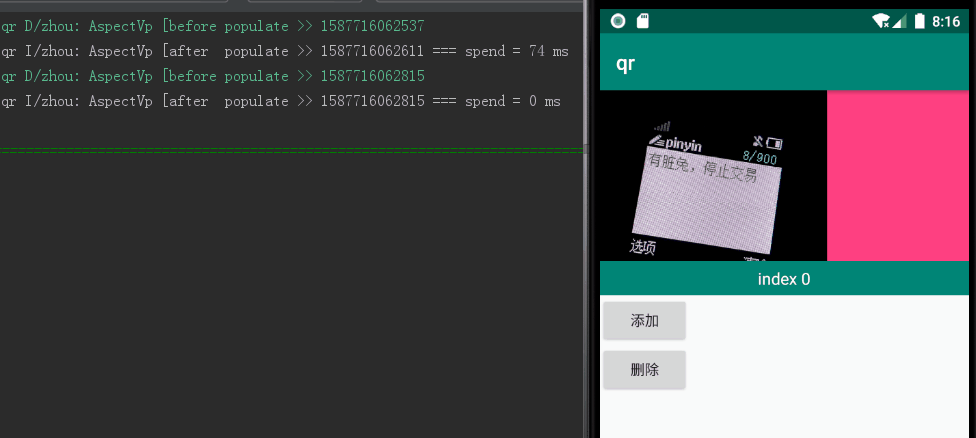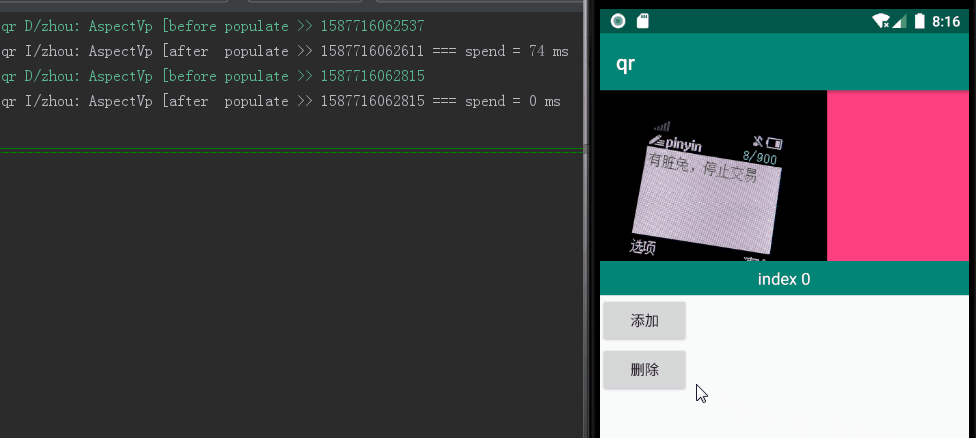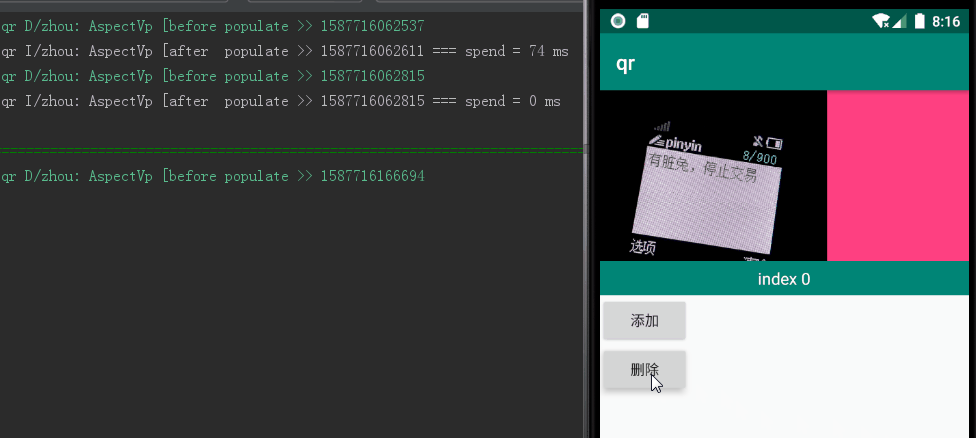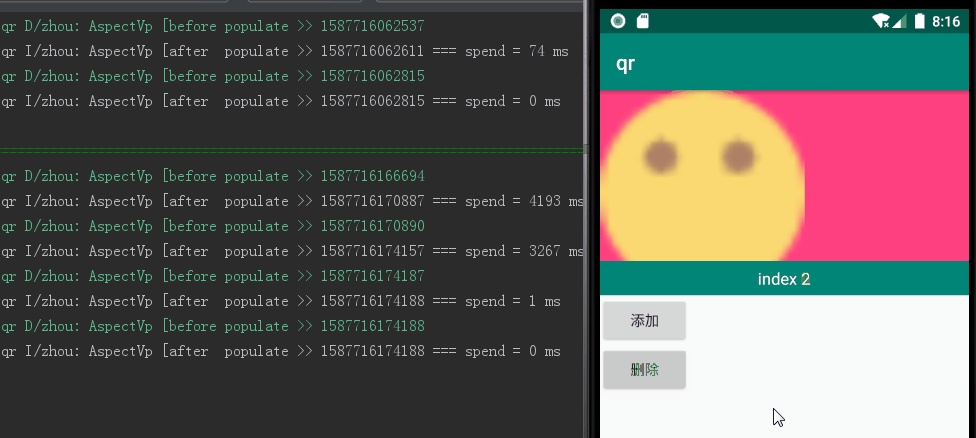
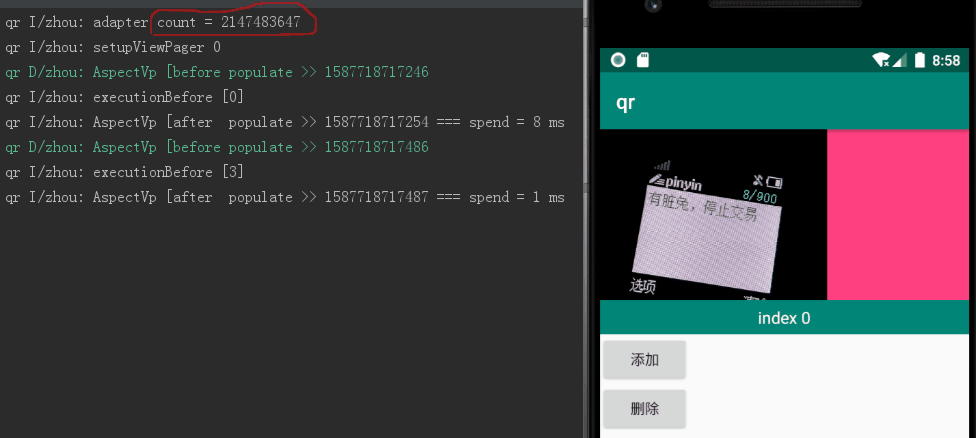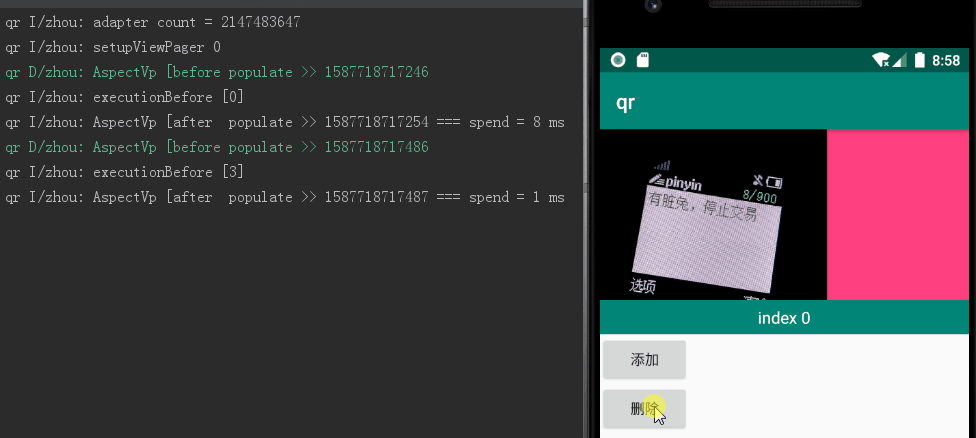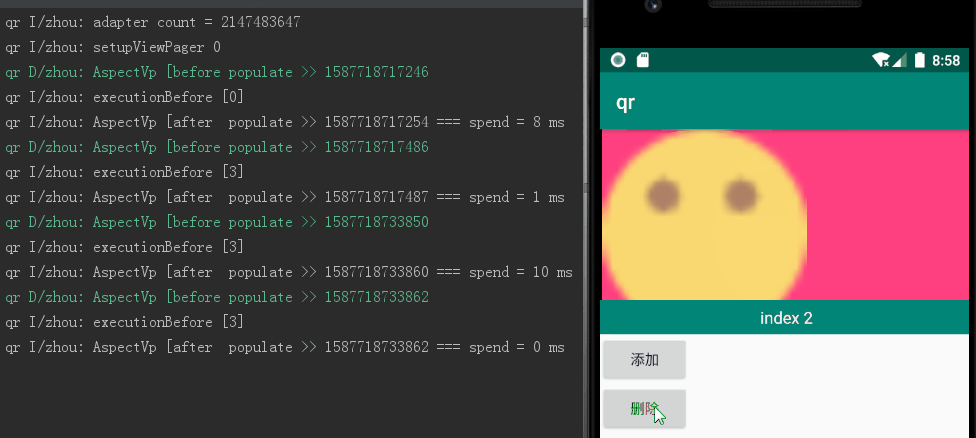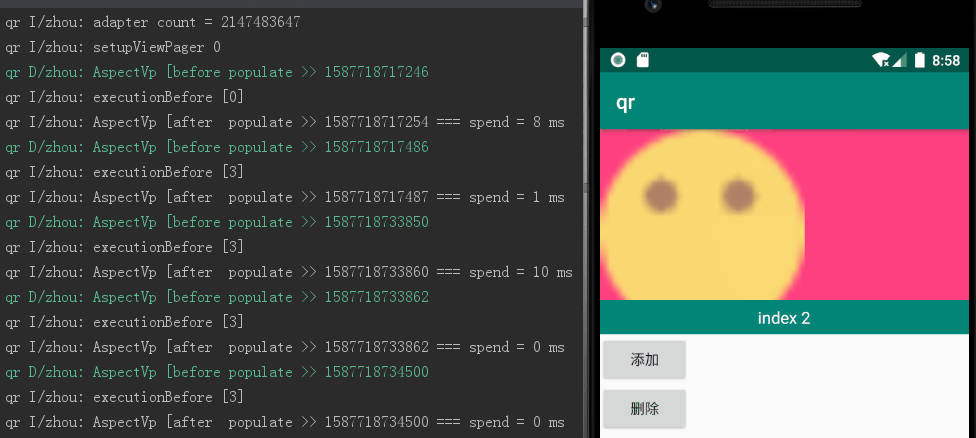
当设置个数为 20000,当前页为10000,跳转到 cur+10 位置,单次执行耗时 1127 ms,如图1所示;4193 ms,如图2所示:
图1:个数 20000
图2:个数 2^32
而且,从日志也可以看出,一次超缓存数的跳转,会触发四次 populate(item) 的调用。
1.setCurrentItem -> 触发 populate(item)
所以,3再会触发一次 populate(),但3-2-3不会成为死循环,总共有4次调用
2.2 解决思路 处理这个问题,有简单的方法,因为设置大数 2^32 真的太大了,修改为小一点、用户感知不强的数字,如10000,而5千次的滑动对用户也算是大操作,并且这个循环耗时在一个可接受范围,也不会造成页面的卡顿甚至 ANR。
或者,当设置的item超过pageLimit,我们强制把 isSrolling 设置为false,那么在遍历缓存 mItem 时能够及时更新 ii,使我们及时打破循环,跳出无用的循环时间。
3. 具体方案:打破循环 打破循环,让 for (int pos = mCurItem - 1; pos >= 0; pos--) 和 for (int pos = mCurItem + 1; pos < N; pos++) 尽快结束循环
3.1 设置有限的小数(相对 2^32 来说) adapter 设置 getCount 为小数值,让循环基数降低,即使执行次数多,所等待的时间也处于可接受范围
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Adapter extends PagerAdapter { //...省略其他代码 @Override public int getCount() { return 10000;//自行设置一个合理的数值 } //...省略其他代码 }
在 setCurrentItem 后,只要设置的 newIndex 在区间 (currentItem-pageLimit,currentItem+pageLimit) ,就不会触发设置该条件,那么在调用设置之前,把 pageLimit 设置为 Math.abs(newIndex - currentItem) ,调用设置位置之后,再重置回去,同样可以达到秒跳转效果,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 //原调用 viewPager.setCurrentItem(newIndex, true); 修改如下 int tmp = viewPager.getOffscreenPageLimit(); int newIndex = viewPager.getCurrentItem() + 10; int newLimit = Math.abs(newIndex-viewPager.getCurrentItem()); if(newLimit>tmp) { viewPager.setOffscreenPageLimit(newLimit); viewPager.setCurrentItem(newIndex, true); viewPager.setOffscreenPageLimit(tmp); }else{ viewPager.setCurrentItem(newIndex, true); }
在设置完 setCurrentItem 后,由于跳转距离问题会将 scrolling 置为 true,所以在执行 void populate(int newCurrentItem) 之前把 scrolling 重置为 false,但是 mItems 是私有变量,需通过反射获取,再通过 AspectJ 埋点在执行之前遍历重置 scrolling,这么看来,无疑方法二是最快解决问题的方式。
以下代码仅供参考,请不要随意应用于生产环境,确定使用请仔细评估性能消耗,完成覆盖测试
!注意:这里的注入对象是所有的 ViewPager!!
代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 @Aspect public class AspectVp { private long time = 0; private static ArrayList<Object> items = null; //反射获取 public static void setupViewPager(ViewPager viewPager) { try { Field field = viewPager.getClass().getDeclaredField("mItems"); field.setAccessible(true); items = (ArrayList<Object>) field.get(viewPager); } catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Log.i("zhou", "setupViewPager " + (items == null ? "null" : items.size())); } //及时销毁 public static void destroyItems() { items = null; Log.i("zhou", "destroyItems "); } @Before("call(void populate(..))") public void beforePopulate(JoinPoint joinPoint) { if (joinPoint.getArgs().length > 0) { Log.d("zhou", "AspectVp [before populate >> " + (time = System.currentTimeMillis())); } } @After("call(void populate(..))") public void afterPopulate(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { if (joinPoint.getArgs().length > 0) { long t = System.currentTimeMillis(); Log.i("zhou", "AspectVp [after populate >> " + t + " === spend = " + (t - time) + " ms"); } } @Before("execution(void populate(..))") public void executionBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { if (joinPoint.getArgs().length > 0 && items != null) { for (Object obj : items) {//强制重置为false Field scrolling = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField("scrolling"); scrolling.setAccessible(true); scrolling.set(obj, false); } Log.i("zhou", "executionBefore [" + items.size() + "]"); } } } //调用 class MainActivity extent Activity{ @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); //省略其他 AspectVp.setupViewPager(viewPager); } @Override protected void onStop() { super.onStop(); //销毁 AspectVp.destroyItems(); } }
运行效果如下:
完。